System Certification
ISO (International Organization for Standardization) is the world's largest developer of standards. ISO identifies what international Standards are required by business, government and society, develops them in partnership with the sectors that will put them to use, adopts them by transparent procedures based on national input and delivers them to be implemented worldwide. ISO is a non-governmental organization and a network of the national standards institutes of 156 countries, on the basis of one member per country, with a Central Secretariat in Geneva, Switzerland, that coordinates the system.
International standardization began in the electrotechnical field: the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) was established in 1906. Pioneering work in other fields was carried out by the International Federation of the National Standardizing Associations (ISA), which was set up in 1926. The emphasis within ISA was laid heavily on mechanical engineering. ISA's activities came to an end in 1942. In 1946, delegates from 25 countries met in London and decided to create a new international organization, of which the object would be "to facilitate the international coordination and unification of industrial standards". The new organization, ISO, officially began operations on 23 February 1947.
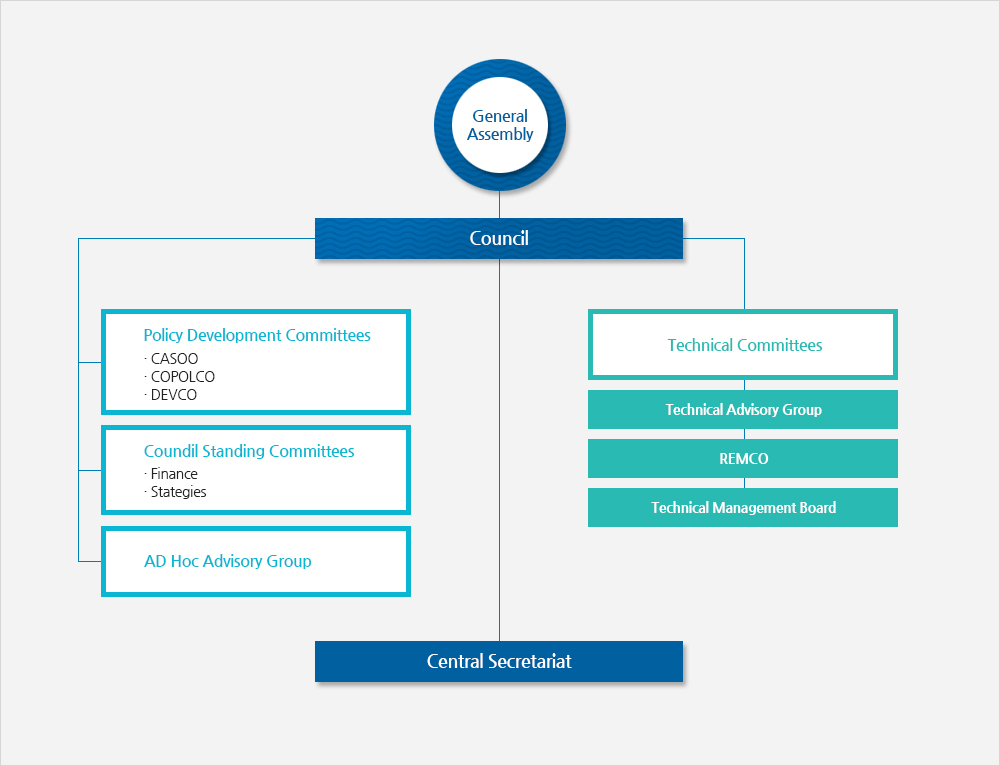
- General Assembly
- Coundil
- Policy Development Committees
- CASOO
- COPOLCO
- DEVCO
- Council Standing Committees
- Finance
- Stategies
- AD Hoc Advisory Group
- Technical Committees
- Technical Advisory Group
- REMCO
- Technical Management Board
- Policy Development Committees
- Central Secretariat